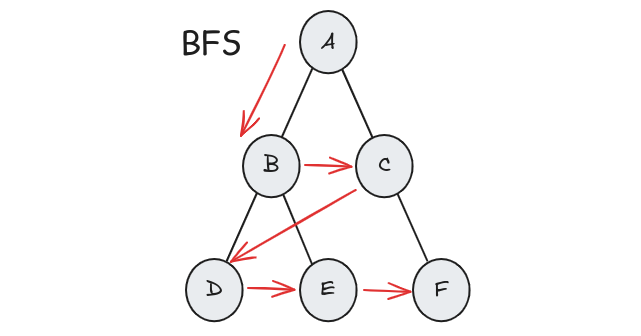
너비 우선 탐색 BFS(Breadth First Search) 정리
너비 우선 탐색 알고리즘(BFS)을 정리합니다.
너비 우선 탐색 BFS(Breadth First Search) 정리
개요
너비 우선 탐색(BFS, Breadth First Search)은 트리 구조 또는 그래프 탐색 방법중 하나입니다. 트리 구조의 루트 노드에서 시작하여 (그래프의 경우 임의의 노드에서 시작하여) 모든 인접 노드를 먼저 탐색한 후, 그 다음 인접 노드를 탐색하는 방식으로 진행하는 알고리즘입니다.
목적
트리 구조 또는 그래프의 모든 노드를 방문하는 데 초점이 맞춰져 있습니다.
주요 특징
탐색 방법
- BFS는 FIFO (First in, First Out) 구조인 큐를 사용하여 탐색 경로를 관리합니다.
- 반복적 방식(iterative)의 구현이 일반적입니다.
탐색 전략
- 시작 노드에서 가까운 노드부터 먼 노드 (레벨) 순서대로 노드를 탐색합니다.
사용 예시
- 트리 구조 또는 그래프의 모든 노드를 방문
- 최단 경로 찾기: 무가중치 그래프에서 출발점에서 목적지까지의 최단 경로 찾기
- 레벨 순서 탐색: 그래프의 각 노드를 레벨별로 방문하기
- 이분 그래프 검사: 그래프가 이분 그래프인지 확인하기(두 개의 그룹으로 나눌 수 있는지 여부)
- 최소 신장 트리: 무가중치 그래프에서 모든 노드를 포함하는 최소 신장 트리 찾기
- 웹 크롤링: 인터넷의 웹 페이지를 순차적으로 탐색하기
- 최단 전파 시간: 네트워크에서 메시지 전파 시간이 가장 짧은 경로 찾기
알고리즘
Iterative BFS
- Initialization
- Start at the root node (or any arbitrary node in the case of a graph).
- Mark the starting node as visited.
- Enqueue the starting node into the queue.
- Exploration:
- If the queue is not empty:
- Dequeue a node from the queue, which is the current node.
- For each unvisited adjacent nodes of the current node:
- Mark the adjacent node as visited.
- Enqueue the adjacent node into the queue.
- If the queue is not empty:
- Termination: Repeat step 2 until all nodes are visited.
Nodes are marked as visited before enqueuing, ensuring they are not enqueued more than once. This approach uses a queue for the BFS and a set to keep track of visited nodes.
의사 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
BFS(graph, start):
create a queue Q
mark start as visited
enqueue start into S
while Q is not empty:
current = Q.dequeue()
// You can add your processing code here
for each neighbor of current:
if neighbor is not visited:
mark neighbor as visited
enqueue neighbor into Q
예제
아래와 같이 두 가지 문제를 풀어본다.
- 간단한 트리 구조
1.1. 문제
1.2. 풀이(iterative) - 간단한 그래프
2.1. 문제
2.2. 풀이(iterative)
1. 간단한 트리 구조
1.1. 문제
아래와 같은 트리에서 BFS 방식을 적용하여 탐색하시오. 탐색은 A 노드에서 시작한다.
graph TD
A---B;
A---C;
B---D;
B---E;
C---F;
1.2. 풀이(iterative approach)
- Initialization
- Start at node A
- Mark node A as visited
- Initialize a queue and enqueue node A into the queue
- Queue: [A]
- Visited: [A]
- Processed: [ ]
graph TD
A---B;
A---C;
B---D;
B---E;
C---F;
style A fill:#9370DB
- Step 1
- Dequeue node A from the queue
- Process(A)
- Enqueue its unvisited adjacent nodes B and C into the queue (order may vary), marking them as visited
- Queue: [B, C]
- Visited: [A, B, C]
- Processed: [A]
graph TD
A---B;
A---C;
B---D;
B---E;
C---F;
linkStyle 0,1 stroke:red
style A fill:#9370DB, stroke:red, stroke-width:2px
style B fill:#9370DB
style C fill:#9370DB
- Step 2
- Dequeue node B from the queue
- Process(B)
- Enqueue its unvisited adjacent nodes D and E into the queue (order may vary), marking them as visited
- Queue: [C, D, E]
- Visited: [A, B, C, D, E]
- Processed: [A, B]
graph TD
A---B;
A---C;
B---D;
B---E;
C---F;
linkStyle 2,3 stroke:red
style A fill:#9370DB
style B fill:#9370DB, stroke:red, stroke-width:2px
style C fill:#9370DB
style D fill:#9370DB
style E fill:#9370DB
- Step 3
- Dequeue node C from the queue
- Process(C)
- Enqueue its unvisited adjacent node F into the queue, marking it as visited.
- Queue: [D, E, F]
- Visited: [A, B, C, D, E, F]
- Processed: [A, B, C]
graph TD
A---B;
A---C;
B---D;
B---E;
C---F;
linkStyle 4 stroke:red
style A fill:#9370DB
style B fill:#9370DB
style C fill:#9370DB, stroke:red, stroke-width:2px
style D fill:#9370DB
style E fill:#9370DB
style F fill:#9370DB
- Step 4
- Dequeue node D from the queue
- Process(D)
- Node D has no unvisited adjacent nodes to enqueue
- Queue: [E, F]
- Visited: [A, B, C, D, E, F]
- Processed: [A, B, C, D]
graph TD
A---B;
A---C;
B---D;
B---E;
C---F;
style A fill:#9370DB
style B fill:#9370DB
style C fill:#9370DB
style D fill:#9370DB, stroke:red, stroke-width:2px
style E fill:#9370DB
style F fill:#9370DB
- Step 5
- Dequeue node E from the queue
- Process(E)
- Node E has no unvisited adjacent nodes to enqueue
- Queue: [F]
- Visited: [A, B, C, D, E, F]
- Processed: [A, B, C, D, E]
graph TD
A---B;
A---C;
B---D;
B---E;
C---F;
style A fill:#9370DB
style B fill:#9370DB
style C fill:#9370DB
style D fill:#9370DB
style E fill:#9370DB, stroke:red, stroke-width:2px
style F fill:#9370DB
- Step 6
- Dequeue node F from the queue
- Process(F)
- Node F has no unvisited adjacent nodes to enqueue
- Queue: [ ]
- Visited: [A, B, C, D, E, F]
- Processed: [A, B, C, D, E, F]
graph TD
A---B;
A---C;
B---D;
B---E;
C---F;
style A fill:#9370DB
style B fill:#9370DB
style C fill:#9370DB
style D fill:#9370DB
style E fill:#9370DB
style F fill:#9370DB, stroke:red, stroke-width:2px
- End
- The BFS traversal order is A → B → C → D → E → F.
2. 간단한 그래프
2.1. 문제
아래와 같은 그래프에서 BFS 방식을 적용하여 탐색하시오. 탐색은 A 노드에서 시작한다.
graph LR
A---B;
A---C;
A----D;
B---C;
C---E;
2.2. 풀이(iterative approach)
- Initialization
- Start at node A
- Mark node A as visited
- Initialize a queue and enqueue node A into the queue
- Queue: [A]
- Visited: [A]
- Processed: [ ]
graph LR
A---B;
A---C;
A----D;
B---C;
C---E;
style A fill:#9370DB
- Step 1
- Dequeue node A from the queue
- Process(A)
- Enqueue its unvisited adjacent nodes B, C, and D into the queue (order may vary), marking them as visited
- Queue: [B, C, D]
- Visited: [A, B, C, D]
- Processed: [A]
graph LR
A---B;
A---C;
A----D;
B---C;
C---E;
linkStyle 0,1,2 stroke:red
style A fill:#9370DB, stroke:red, stroke-width:2px
style B fill:#9370DB
style C fill:#9370DB
style D fill:#9370DB
- Step 2
- Dequeue node B from the queue
- Process(B)
- Node B has no unvisited adjacent nodes to enqueue
- Queue: [C, D]
- Visited: [A, B, C, D]
- Processed: [A, B]
graph LR
A---B;
A---C;
A----D;
B---C;
C---E;
linkStyle 3 stroke:grey
style A fill:#9370DB
style B fill:#9370DB, stroke:red, stroke-width:2px
style C fill:#9370DB
style D fill:#9370DB
- Step 3
- Dequeue node C from the queue
- Process(C)
- Enqueue its unvisited adjacent node E into the queue, marking it as visited.
- Queue: [D, E]
- Visited: [A, B, C, D, E]
- Processed: [A, B, C]
graph LR
A---B;
A---C;
A----D;
B---C;
C---E;
linkStyle 4 stroke:red
style A fill:#9370DB
style B fill:#9370DB
style C fill:#9370DB, stroke:red, stroke-width:2px
style D fill:#9370DB
style E fill:#9370DB
- Step 4
- Dequeue node D from the queue
- Process(D)
- Node D has no unvisited adjacent nodes to enqueue
- Queue: [E]
- Visited: [A, B, C, D, E]
- Processed: [A, B, C, D]
graph LR
A---B;
A---C;
A----D;
B---C;
C---E;
style A fill:#9370DB
style B fill:#9370DB
style C fill:#9370DB
style D fill:#9370DB, stroke:red, stroke-width:2px
style E fill:#9370DB
- Step 5
- Dequeue node E from the queue
- Process(E)
- Node E has no unvisited adjacent nodes to enqueue
- Queue: [ ]
- Visited: [A, B, C, D, E]
- Processed: [A, B, C, D, E]
graph LR
A---B;
A---C;
A----D;
B---C;
C---E;
style A fill:#9370DB
style B fill:#9370DB
style C fill:#9370DB
style D fill:#9370DB
style E fill:#9370DB, stroke:red, stroke-width:2px
- End
- The BFS traversal order is A → B → C → D → E.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.